What is CBC Cannabinoid? A Comprehensive Guide
Explore unique properties and benefits of CBC.
Explore unique properties and benefits of CBC.
Introduction: What Are Cannabinoids?
Cannabinoids are intricate chemical compounds found naturally in the cannabis plant. They play a crucial role in interacting with the body's endocannabinoid system. This system regulates a wide array of bodily functions such as pain, inflammation, mood, and appetite.
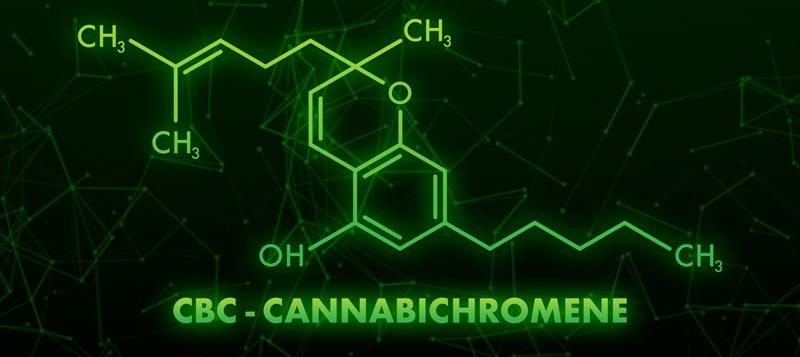
What is CBC (Cannabichromene)?
Cannabichromene, often abbreviated as CBC, is a non-psychoactive cannabinoid that is among the most abundant in the cannabis plant, following CBD and THC and several others. While CBC shares structural similarities with CBD, their properties differ significantly.
- CBC was first isolated in 1966 by Raphael Mechoulam and Yechiel Gaoni.
- CBC is a white or colorless oil that is soluble in alcohol and ether.
- CBC is generally considered to be safe, but there have been some reports of side effects such as nausea and vomiting.
Will CBC Get You High?
Unlike THC, the primary psychoactive compound in cannabis, CBC does not produce mind-altering effects. It doesn’t bind to the brain's CB1 receptors the way THC does. Therefore, it won't get you "high."
How CBC Interacts with Other Cannabinoids
CBC's versatility is highlighted by its multiple potential benefits. Current research indicates that CBC possesses anti-inflammatory, analgesic, and anti-cancer properties. More intriguingly, it seems to function synergistically with other cannabinoids, enhancing the effects of compounds like CBD and THC.
CBC vs. CBD vs. CBG: Understanding the Differences
CBC, CBD, and CBG are all non-psychoactive cannabinoids derived from the cannabis plant, making them appealing options for those seeking therapeutic benefits without the "high" associated with THC. While they share certain similarities, it's essential to appreciate their unique properties and effects.
- CBC: Less studied than CBD, CBC is gaining attention for its potential applications, but research is in its early stages.
- CBD: The most well-known and extensively researched, CBD has established a reputation for various applications beyond its therapeutic attributes.
- CBG: Often dubbed the "mother" cannabinoid, CBG is the precursor from which other cannabinoids form. Its research is still budding, but early indications suggest it has unique properties distinct from CBD and CBC.
In essence, while they all belong to the same cannabinoid family, CBC, CBD, and CBG each have their own unique profile, warranting further exploration.
What Are the Benefits of CBC
Emerging studies point towards several potential medical benefits of CBC:
- Pain relief: Animal studies are increasingly showing CBC's potential in pain management.
- Anti-inflammatory: Conditions like arthritis and inflammatory bowel disease might benefit from CBC's strong anti-inflammatory actions.
- Anti-cancer: Preliminary research suggests CBC can hamper the growth of tumor cells.
- Appetite stimulation: For those struggling with anorexia, CBC could serve as an appetite stimulant.
- Neuroprotection: Protecting brain cells from potential damage, CBC might be pivotal in tackling neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer's and Parkinson's.
Conclusion: The Future of CBC
Cannabichromene (CBC) is emerging as a cannabinoid with vast therapeutic potential. While the journey to fully fathom its health implications is ongoing, CBC continues to solidify its position as a valuable component in the medical cannabis toolkit.
Health Disclaimer: The information provided in this article is for educational purposes only and should not be taken as medical advice. Always consult with a qualified healthcare provider before using cannabis, particularly if you have pre-existing conditions or are taking medication.